Modern UK homes are increasingly embracing smart technology, but choosing the right home automation controller can be overwhelming with various protocols, compatibility requirements, and system architectures available. The market offers everything from comprehensive central hubs to specialised device controllers, each serving different roles in creating a cohesive smart home experience.
This comprehensive guide explores different types of home automation controllers, from central gateway hubs to specialised motor and lighting controllers, helping you build a cohesive smart home ecosystem that meets UK standards and regulations. Understanding the distinctions between controller types enables you to make informed decisions that enhance both functionality and long-term value.
You'll learn about controller types, compatibility considerations, integration strategies, and practical implementation steps to create a future-proof home automation system tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're starting fresh or expanding an existing setup, this guide provides the technical knowledge and practical insights necessary for successful implementation.
Understanding Home Automation Controllers: Types and Functions
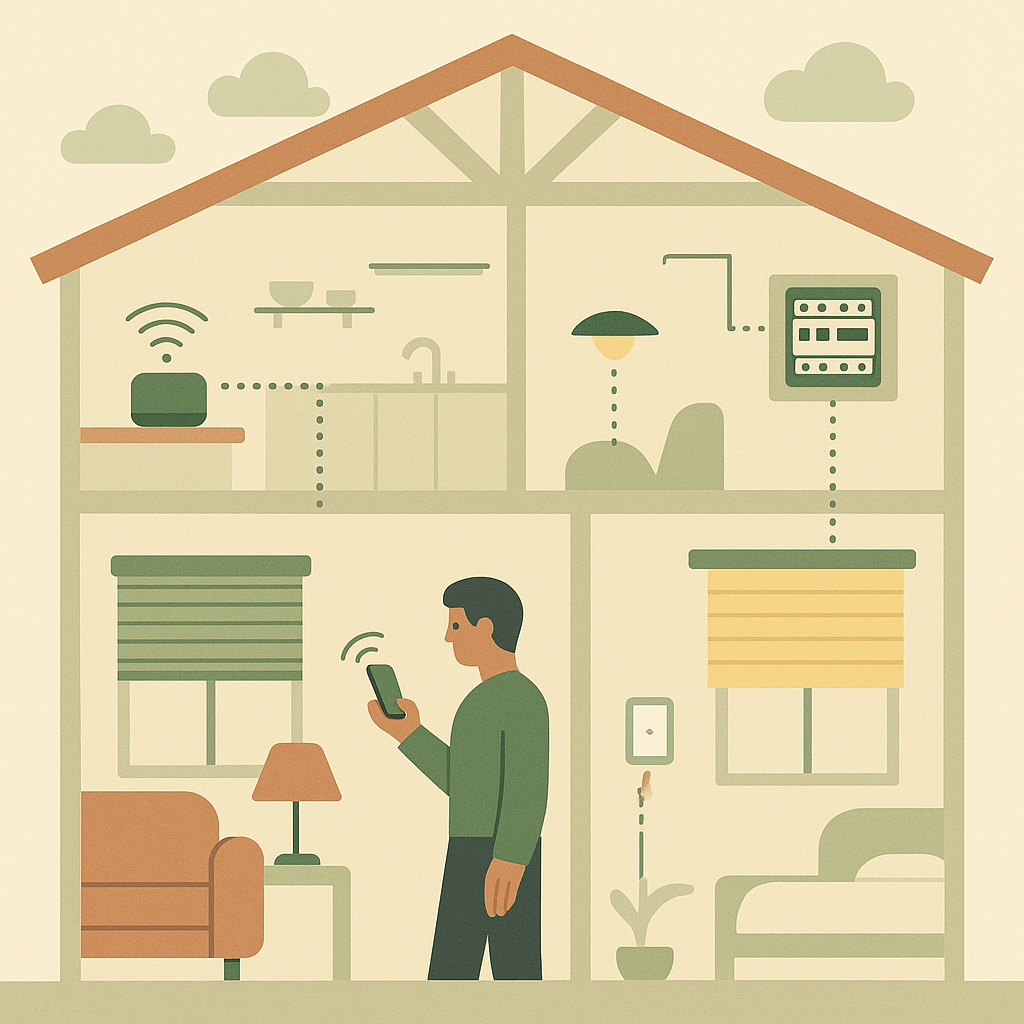
Home automation controllers serve as the communication backbone between smart devices and users, but not all controllers perform the same function. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the right combination for your specific requirements and budget.

Primary controller categories:
- Gateway hubs that centralise communication across multiple protocols
- Dedicated device controllers for specific applications like lighting or motors
- DIN rail modules for professional installations and electrical panels
- Handheld remotes for immediate local control and system management
Each controller type integrates differently within your home automation systems architecture. Gateway controllers typically manage the entire ecosystem, whilst specialised controllers handle specific device categories or room-by-room control scenarios with greater precision and reliability.
Gateway Hubs: The Central Command of Your Smart Home
A home automation hub functions as the central nervous system of your smart home, translating commands between different protocols and enabling unified control through single applications. These multi-protocol controllers support Z-Wave, Zigbee, Wi-Fi, and often proprietary wireless standards simultaneously.
Gateway hubs excel at creating automated scenarios that span multiple device types and manufacturers. They maintain device databases, manage security protocols, and provide remote access capabilities that allow control from anywhere with internet connectivity.

Key gateway hub capabilities:
- Multi-protocol communication supporting Z-Wave, Zigbee, and Wi-Fi devices
- Cloud connectivity enabling remote monitoring and control
- Local processing for reduced latency and improved reliability
- Integration with voice assistants and third-party platforms
Specialised Controllers for Different Home Systems
While gateway hubs provide centralised control, specialised home automation controllers offer targeted functionality for specific applications. Motor controllers manage blinds, curtains, and garage doors with precise positioning and feedback capabilities that general-purpose hubs cannot match.
Common specialised controller applications:
- Smart dimmers providing advanced lighting control with scene programming
- Motor controllers for automated window coverings and access control
- DIN rail modules integrating with professional electrical installations
- Sensor controllers managing environmental monitoring and security systems
These controllers often provide better performance and reliability for their specific applications compared to relying solely on a central hub. They're particularly valuable in scenarios requiring immediate response times or precise control parameters that benefit from dedicated processing power.
UK Compliance and Standards: What You Need to Know
UK home automation systems must comply with specific electrical regulations, wireless frequency allocations, and building standards. The 18th Edition Wiring Regulations require proper circuit protection and documentation for smart home installations, particularly when integrating controllers into existing electrical systems.
Wireless protocols used by home automation controllers operate within Ofcom-regulated frequency bands. Z-Wave operates at 868.42 MHz, whilst Zigbee uses the 2.4 GHz ISM band, both requiring compliance with UK electromagnetic compatibility standards for reliable operation.
Essential UK compliance considerations:
- CE marking and UKCA conformity for wireless controllers
- Part P Building Regulations for electrical installations
- Energy efficiency requirements under UK building standards
- Data protection compliance for connected home systems
System Planning and Integration Strategy
Successful home automation controller implementation begins with thorough planning that considers current needs, future expansion possibilities, and integration requirements. Start by mapping your home's layout and identifying areas that would benefit most from automated control.

Critical planning considerations:
- Wireless signal coverage and potential interference sources
- Power requirements and electrical infrastructure capabilities
- Device compatibility across different manufacturer ecosystems
- Scalability pathways for future system expansion
Consider how different controller types will work together within your overall architecture. A central home automation hub might handle routine scheduling and automation, whilst specialised controllers manage critical functions like security systems or climate control that require immediate response.
Installation and Setup Best Practices
Proper installation ensures reliable operation and maximises the performance of your home automation controller system. Begin by establishing a robust wireless network foundation, positioning controllers to optimise signal coverage whilst avoiding interference from other household electronics.
Most gateway hubs require ethernet connectivity for initial setup and optimal performance, even when supporting wireless protocols. Plan controller placement to maintain reliable connectivity whilst ensuring accessibility for maintenance and troubleshooting.

Installation best practices:
- Position hubs centrally with minimal obstructions to wireless signals
- Use dedicated power supplies rather than sharing outlets with high-interference devices
- Document device pairings and network configurations for future reference
- Test all communication paths before finalising mounting locations
Advanced Features and Automation Scenarios
Modern home automation controllers enable sophisticated scenarios that adapt to your lifestyle patterns and preferences. Advanced systems learn from user behaviour, adjusting lighting, temperature, and security settings automatically based on occupancy patterns and time-of-day preferences.
Advanced automation possibilities:
- Geofencing capabilities that trigger actions based on location
- Energy management integrating solar panels and battery storage
- Security protocols linking cameras, sensors, and lighting systems
- Voice control integration with natural language processing
Integration between multiple controller types creates particularly powerful automation scenarios. For example, a motor controller managing window blinds can coordinate with lighting controllers and HVAC systems to optimise natural light usage and energy efficiency throughout the day.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Regular maintenance keeps home automation systems running smoothly and prevents common issues before they disrupt daily routines. Most controller problems stem from connectivity issues, outdated firmware, or incorrect device configurations that develop over time.
Establish routine maintenance schedules that include firmware updates, battery replacements for wireless devices, and network performance testing. Document any changes or additions to help troubleshoot future issues quickly.
Common troubleshooting steps:
- Restart controllers and check network connectivity first
- Verify device batteries and wireless signal strength regularly
- Update controller firmware and device drivers periodically
- Reset and re-pair devices experiencing persistent connectivity issues
Conclusion
Selecting the right home automation controller system transforms your UK home into an intelligent, efficient, and secure living space. From central gateway hubs that orchestrate your entire smart ecosystem to specialised controllers for lighting, motors, and sensors, the key is choosing components that work together seamlessly whilst meeting UK standards and your specific needs.
Start your smart home journey by assessing your current setup and identifying which areas would benefit most from automation. Whether you begin with a comprehensive gateway hub or focus on specific room controllers, building your system incrementally allows you to learn and expand at your own pace whilst ensuring each addition integrates smoothly with your existing setup.
Ready to explore home automation controllers for your smart home? Browse our extensive range of gateway hubs, specialised controllers, and integration devices to find the perfect foundation for your automated home. Our expert team is here to help you navigate the options and create a system that grows with your needs whilst delivering the convenience, security, and efficiency you're looking for.